More actions
| Samsung Galaxy A03s CPU Swap Step by Step Guide | |
|---|---|
| Type | Method |
| Device(s) | Galaxy A03s |
| Difficulty | ◉◉◉◉ Specialist |
Problem description
If you have a Samsung A03s that does not boot up, and all other efforts to fix the existing board has failed, then you can follow this guide on how to swap the paired chips onto another working board for the purposes of recovering the data that's trapped inside the chips.
🚨 Please Note 🚨
This process is super risky & requires tons of practice & skill to successfully do it.
If you damage the CPU or the UFS (Storage) chip, then it's game over. The data is gone forever.
So do not try this if you have no experience with CPU Swaps.
Absolutely DO NOT try this if you have no microsoldering experience.
I would recommend you practice on donor motherboards & once you can do it successfully 3 in a row, then you should have enough experience to do this on a live customer's board.
Recommended Tools
Hot Air Station: Atten ST-862D with 13mm Bent Nozzle
Soldering Iron: Aixun T420D with T210 Handle & JBC C210018 Knife Tip
Symptoms
- No Power
- Does not boot up
- No signs of life
- Board is cracked
- Board is water damaged beyond repair
Solution
Repair Steps
First, you need to locate the CPU and UFS.
- CPU holds the encryption keys
- UFS has the data, but it's encrypted
Both chips MUST be fully working & not damaged/cracked.
These chips talk to each other & during bootup, they exchange the keys so the phone can decrypt the data after the pin code is entered. Without the pin code, data cannot be decrypted & accessed.
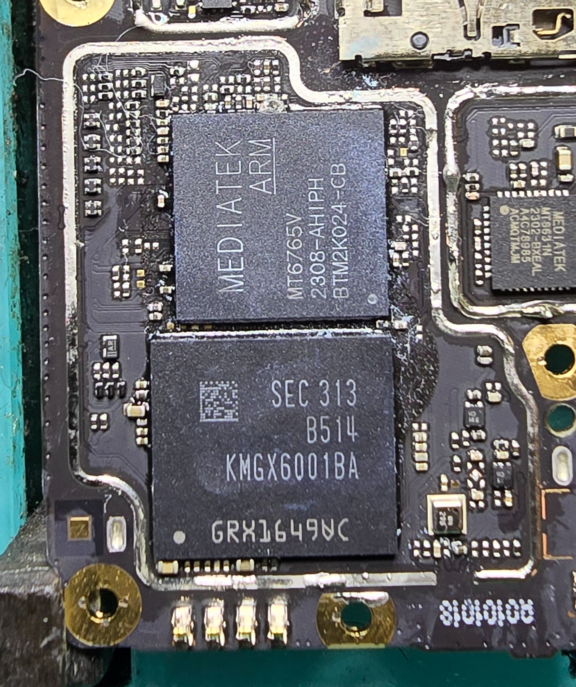
Here's a picture of where these chips are:
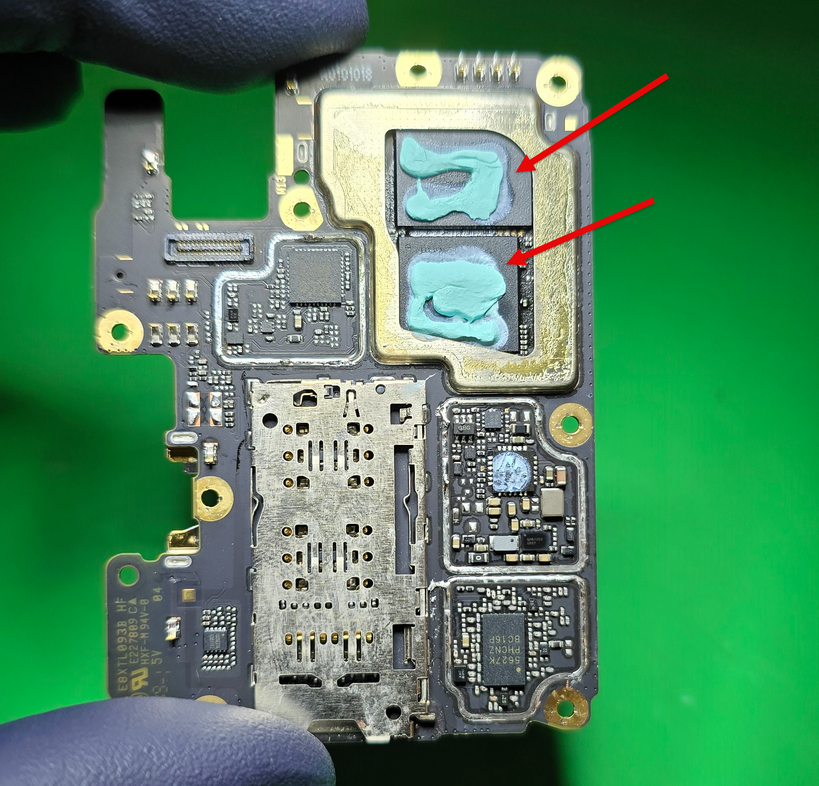
Typically, these are next to each other & very large chips. They also tend to have thermal paste or thermal pads. Sometimes they have shields completely covering them.
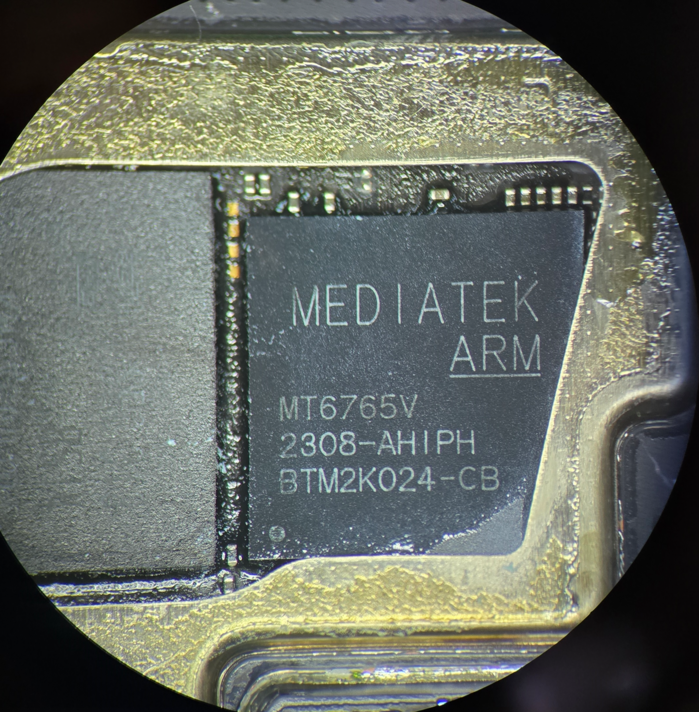
On this model, the CPU is labeled as MediaTek. So we can assume the other chip is the UFS.
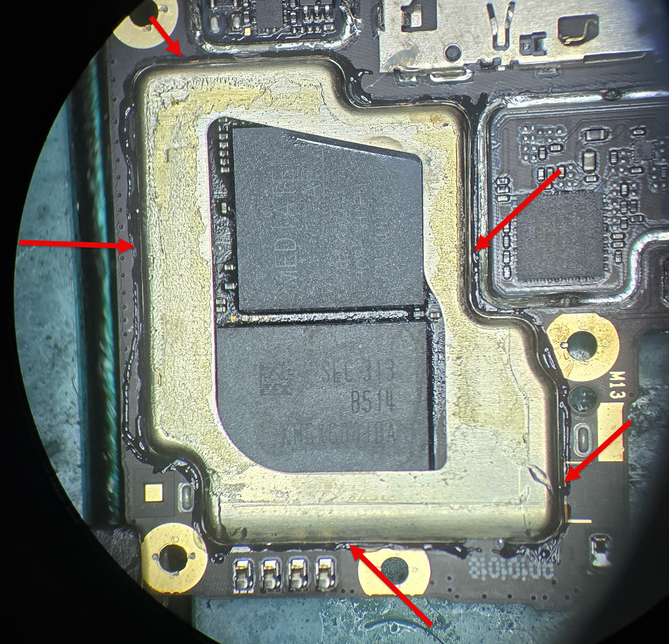
Now we must remove the shield around it to access the chips. I would recommend adding 138C Ultra Low Melt solder to the solder joints where the shield is attached to the board. Make sure to add plenty of flux & use a knife tip style iron
This will make removing the shield much easier
Using high temps, like 400C/60 air, heat around the perimeter
Use a hook tool or tweezers to grab onto the shield & pull it up, until it detaches, like this:
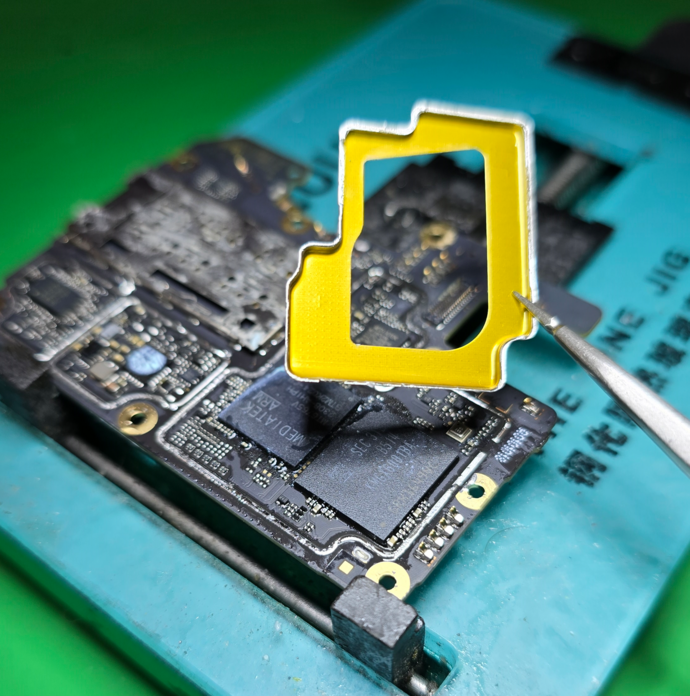
And now you have clear access to the 2 chips you need.

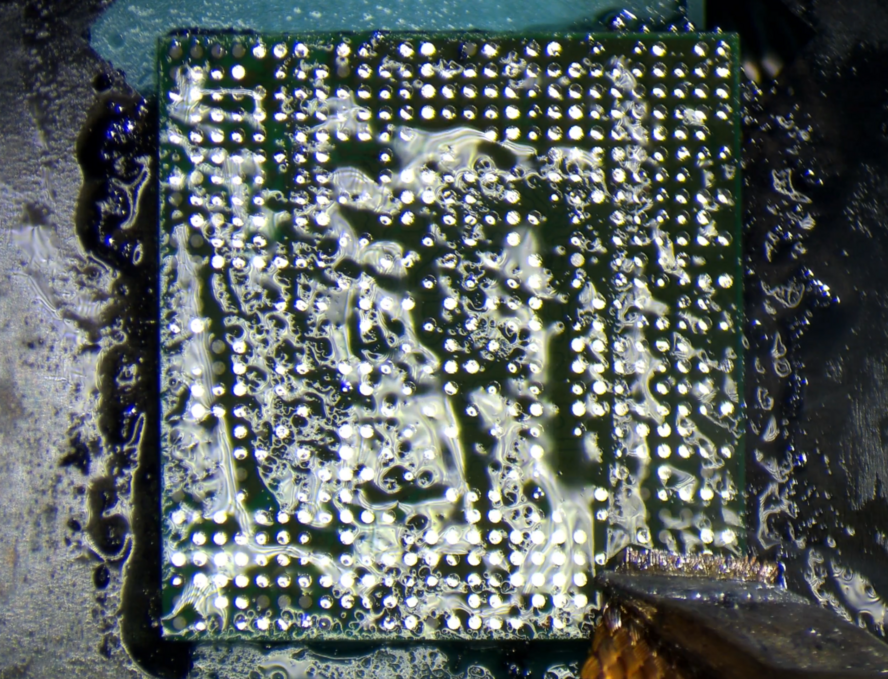
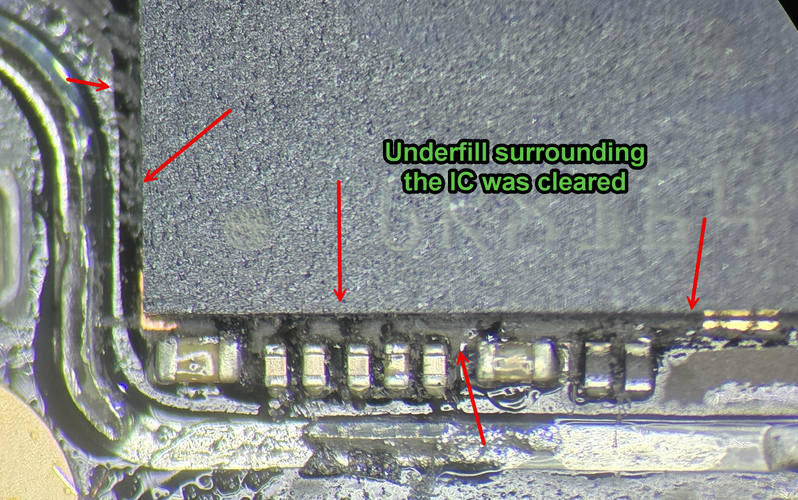
The CPU and UFS chips have hard & rubbery "glue" like substance that has these chips sealed to the board. This stuff is called "underfill". It must be cleared out with a sharp blade, like Scalpel #11 blade.

Go around all 4 sides of the CPU and UFS & get rid of it. This makes it so you can lift the chips easiest.
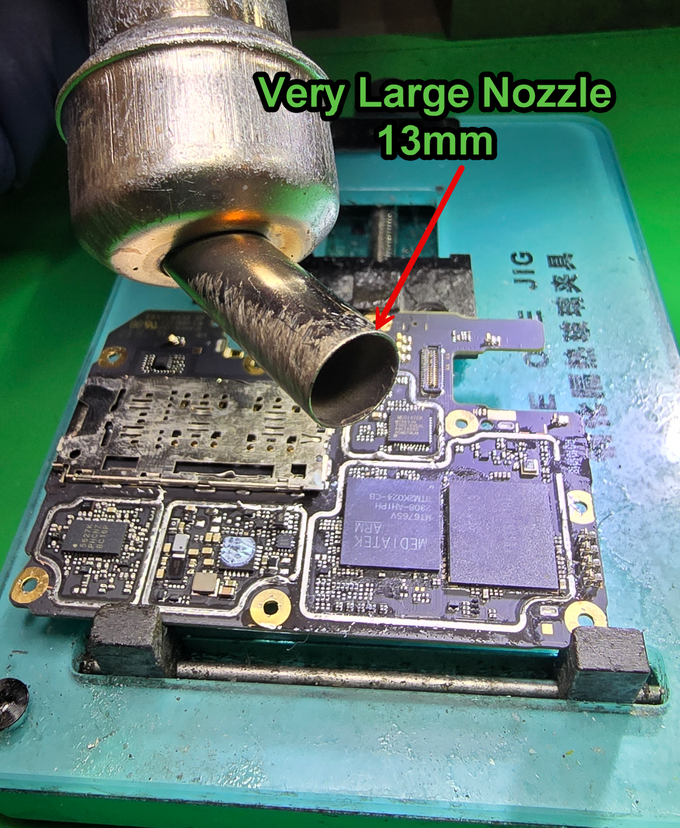
Switch to the largest nozzle your hot air station can support. For the Atten, we are using a bent 13mm nozzle
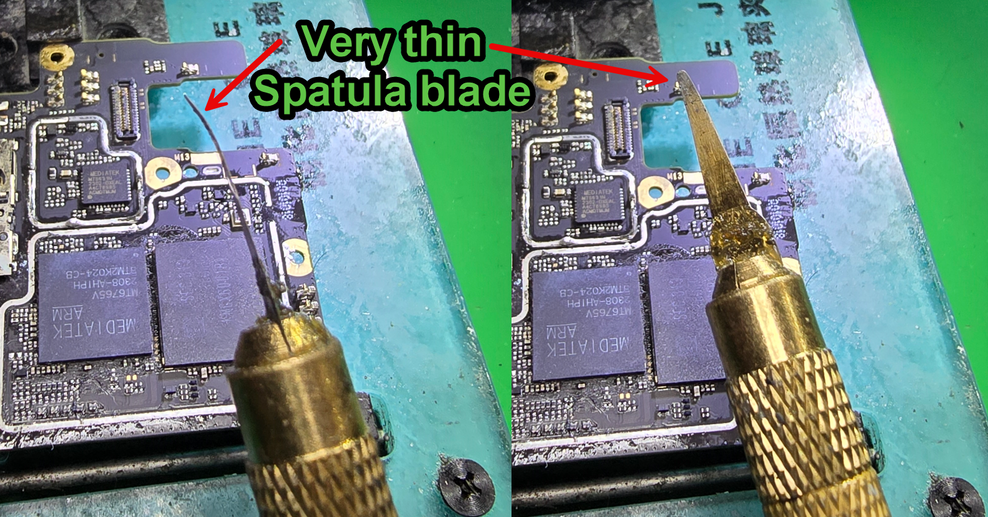
You're also going to need a very thin spatula blade. Use sandpaper to thin it out even further. Ideally, you'll want to taper the tip. This allow the blade to enter under the chip safely & cut through the underfill
You'll want to use around 380C-400C to heat the chip in a circular motion. Make sure to start off far away, about 6in and heat in circles. This is to first warm up the board.
Over a 30 second period, get closer & closer until you're about 2-4mm away and always keep moving in circles.
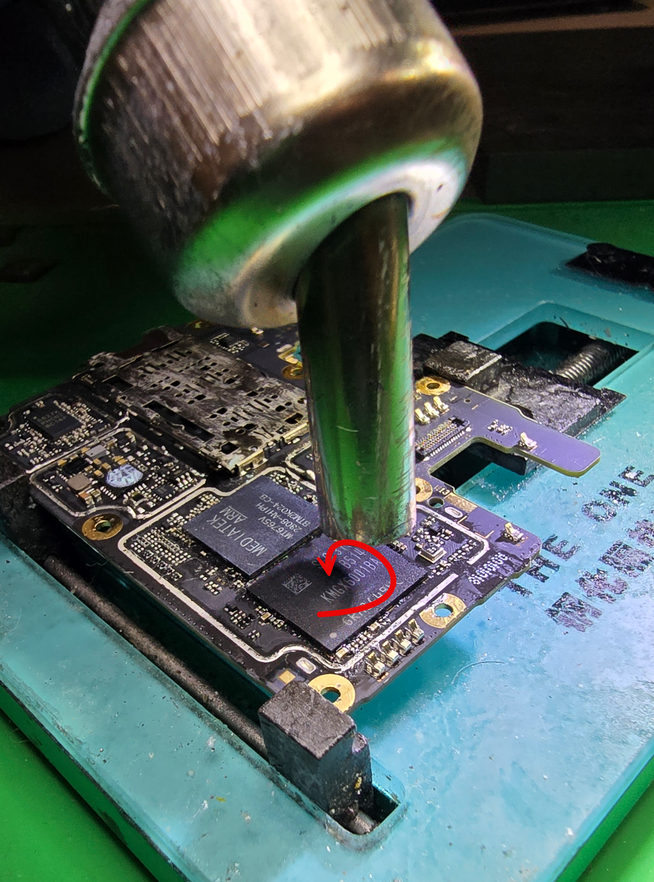

After about 30 seconds, the board should be very hot. This will make the underfill very soft.
Make sure to keep heating the IC in circles while still in close proximity.
Find an entry point, where there's no components and gently try to pry into the chip. But only go in horizontally. Maybe a little angled to try to get under, but stay as horizontal as possible
If you don't feel it budge, then don't force it in. Although some force is required, there's a fine point on what's too much. This is where lots of practice comes in to know what proper force is
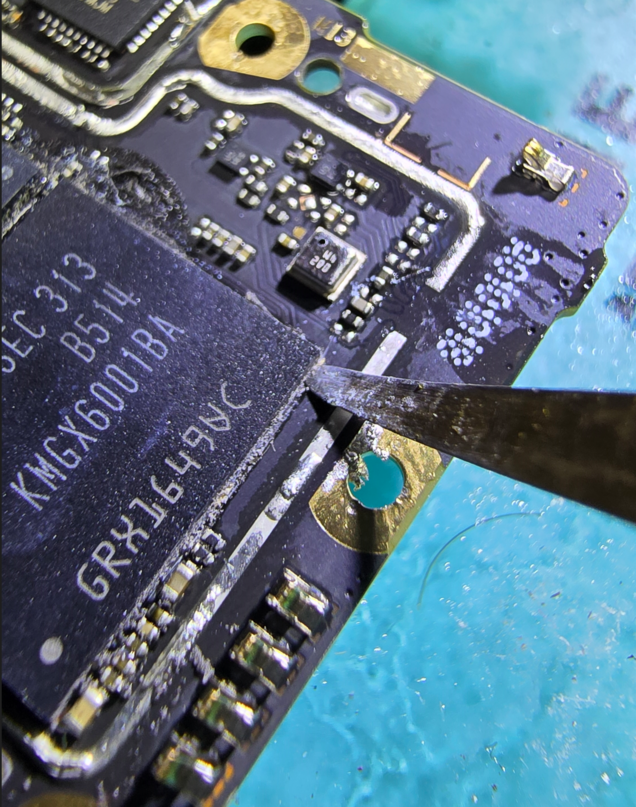
.As the spatula starts entering, do slicing motions, in and out. But do it gently.
You should be at about 60-90 seconds into this by this point.
If you're not having luck entering under the chip, try turning your temps & air flow up by 10 points and try again.
Don't heat the chip more than 2 or 3 minutes at a time. Reasses the situation & see if you need to adjust your temps more. If your tool is too thick. If maybe there's a better spot to enter.
Whatever you do, do not bend the chip up trying to remove it. You can damage it permanently & lose all chance to get data.
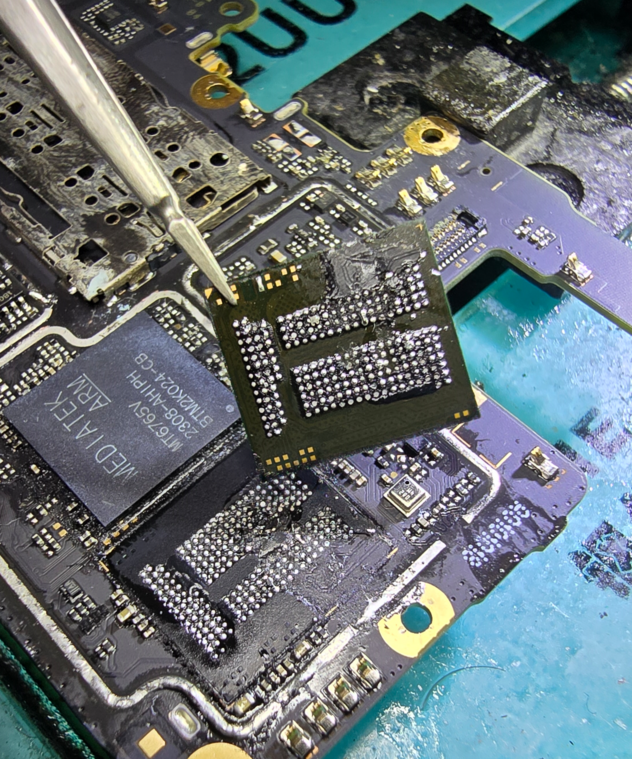
Once the chip is removed, inspect it for any damage. Look closely for any ripped pads or any scratches on the IC. This is where most go wrong & damage the chip. In many cases, if the chip gets damaged, then it's game over.
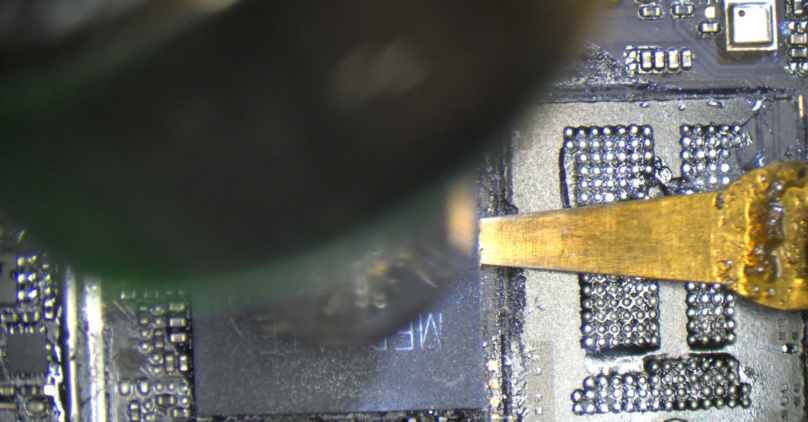
Then you'll have to repeat the same steps to ultimately remove the 2 important chips: CPU and UFS

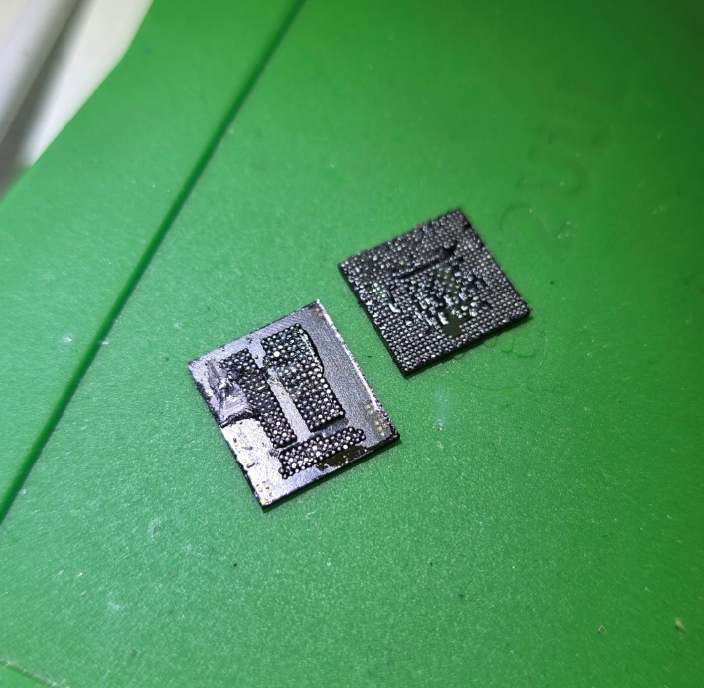
Make sure to save these 2 chips. They are paired together & must be installed onto the working donor board. I would suggest to have a designated spot on your bench, like a small tin can or box, where you will always place the critical customer chips into, so you don't mix them up with the donor board chips.
Then, we must prep the donor board.
Start by removing the same 2 chips, but this time, we are saving the board & throwing away the CPU and UFS from the donor board.
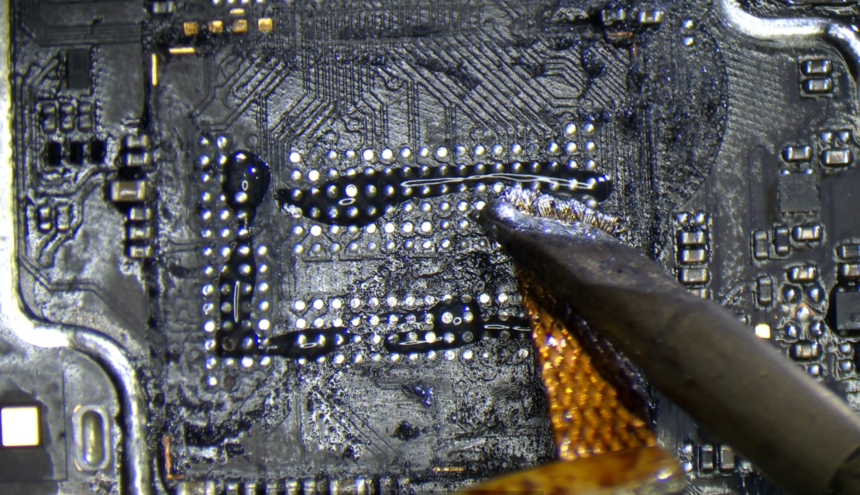
After removing the chips, we must prep the board.
Using hot air at 250C / 40 air flow, pick off all the big chunks of underfill off the board. You can use your tweezers, scalpel blade or other pointy tool to pick it off. The hot air will soften it so it comes off really easy.
Then you want to add tons of flux on the board & run your iron with a big blob of low melt solder (138C), over all the pads. Make sure all pads get covered with the new solder.
Make sure to clean the board thoroughly with iso and toothbrush.
Now, add tons of flux again & wick all the pads flat. Then clean the board again.
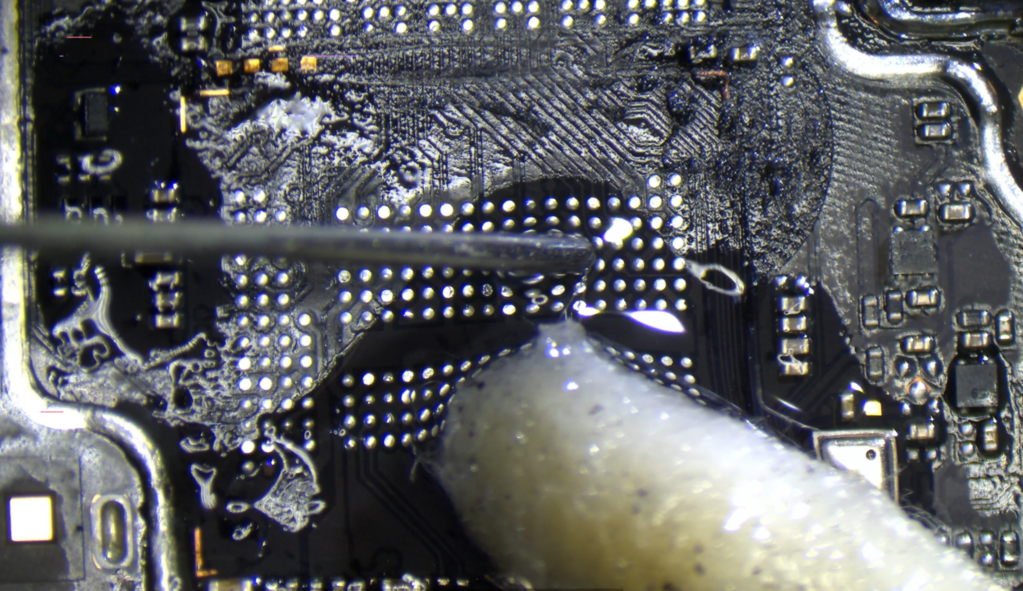

Repeat this for both CPU and UFS pads. Make sure every speck of underfill is removed. This will ensure the chips sit evenly & flat.

Next step is to prep the customer's chips: CPU and UFS
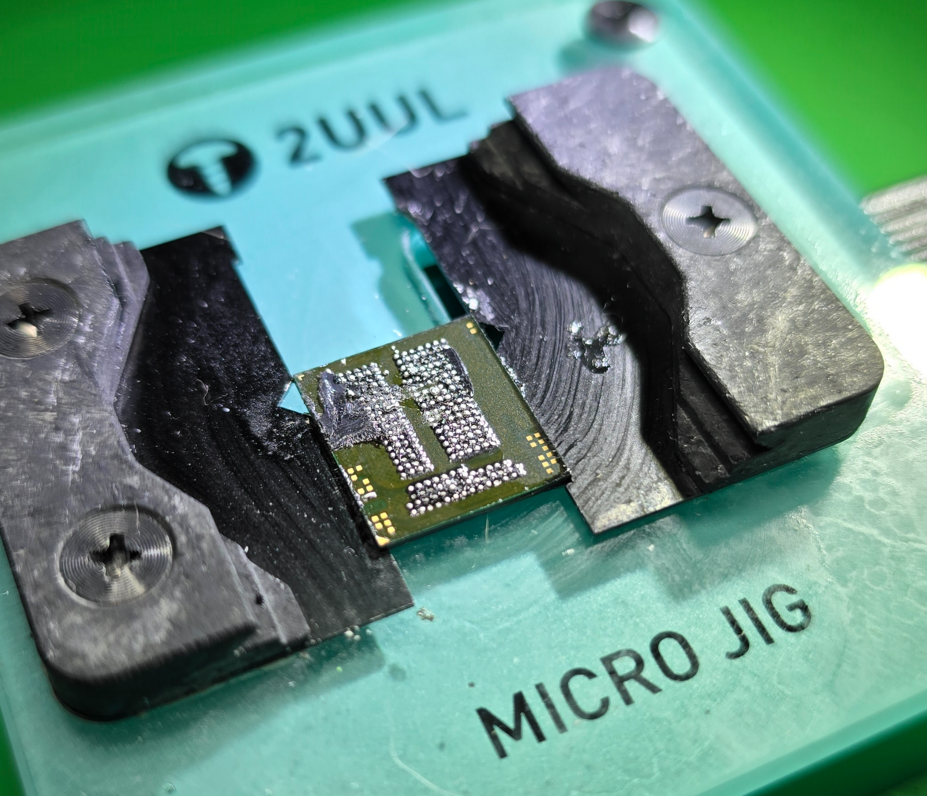
Use a jig, like the 2uul Micro Jig, to hold the IC facing up. As it makes it easier to work on the chip. We have to clean off all the underfill, prep the pads & wick them flat.
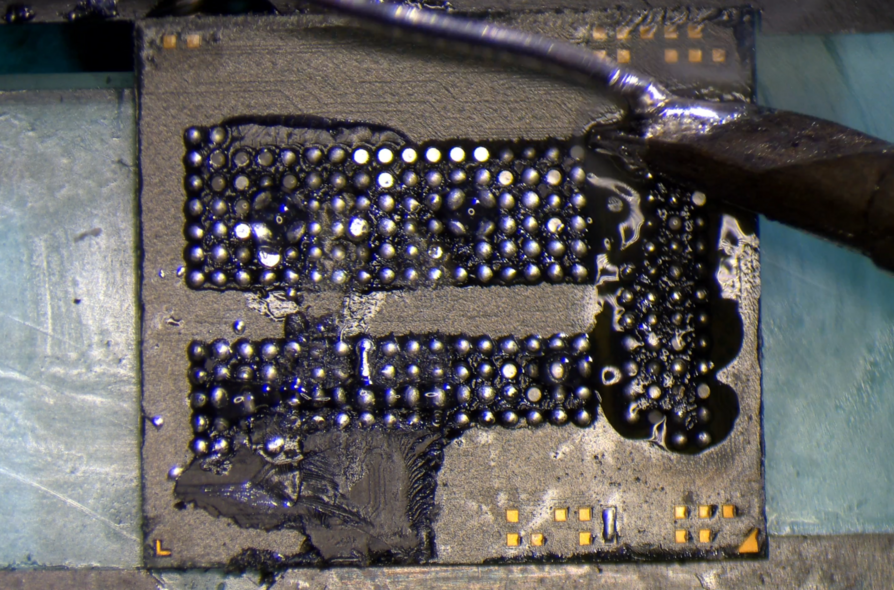
Add lots of flux then use 138C low melt solder to run over all the pads.
Then add more flux & do it again.
The goal is to clean off as much of the underfill as possible.
You can use hot air & a scalpel blade to pick off any small remnants of underfill, if necesary.

And make sure to clean off all the burnt flux regularly using iso & q-tips.
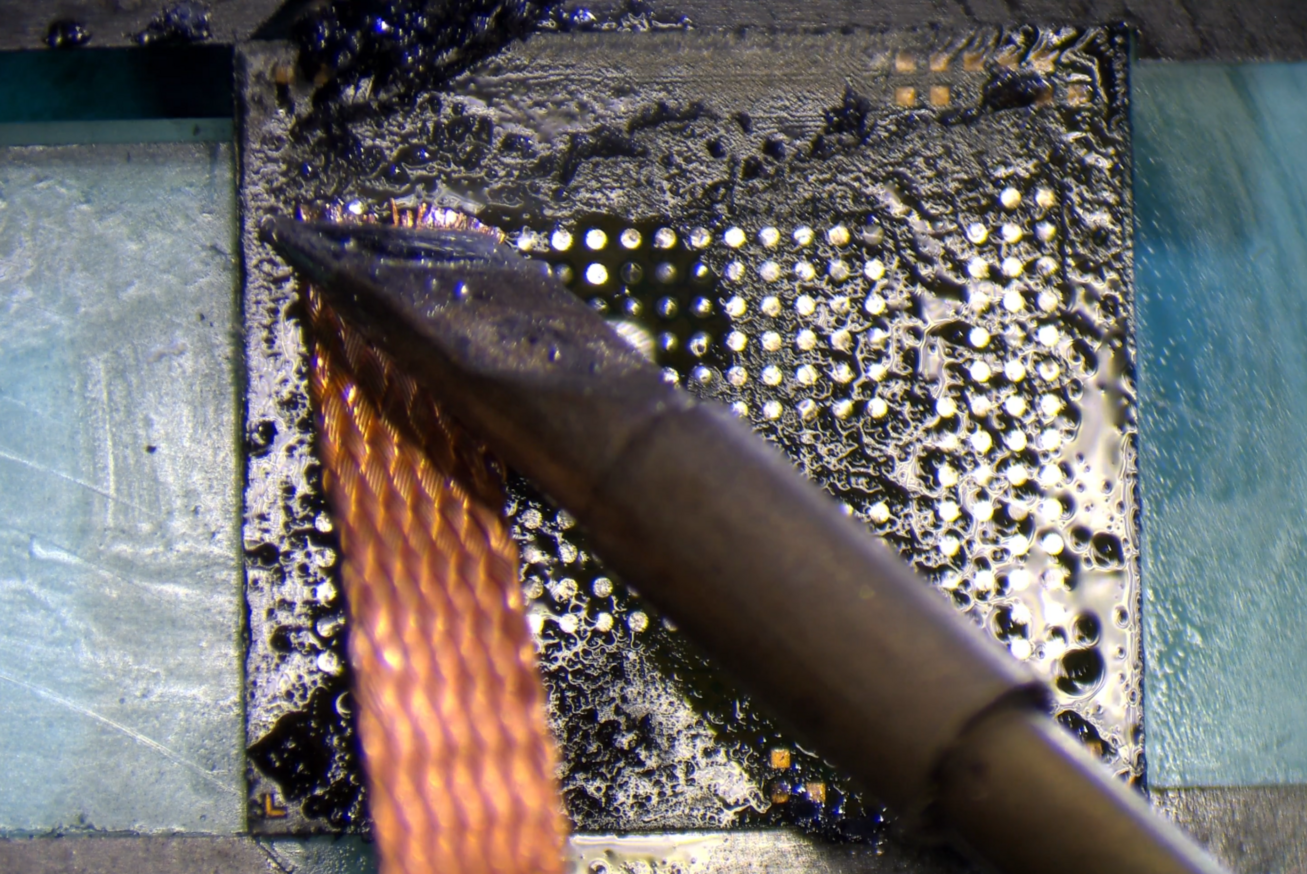
Lastly, you'll want to wick the chip flat. This allows for better results when reballing a large IC like CPU and UFS.
Repeat the same steps for the CPU.
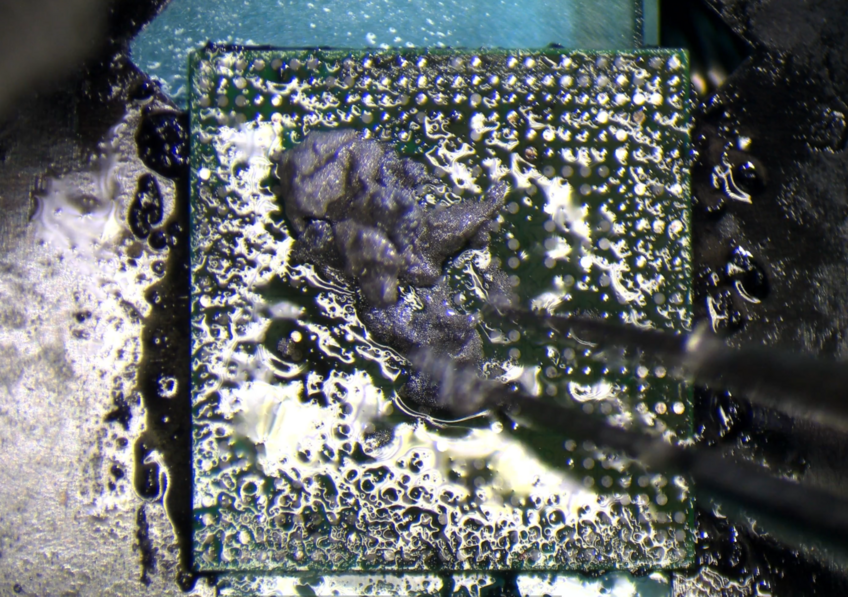
If the chip has a lot of oxidized pads (pads that are dark gray & are not taking in any solder), you can use try this trick.
Add flux & solder paste to the chip

Make sure to spread it across the whole chip

Then use hot air to melt the solder at 320C / 25 air.
Once the solder paste has melted & turned into solder balls, you can run your iron over all the pads.
You'll see a bit portion of the oxidized pads are gone.